CoNS
Emery Haley, PhD, Scientific Writing Specialist
Coagulase-negative Staphylococci Group
Clinical Summary
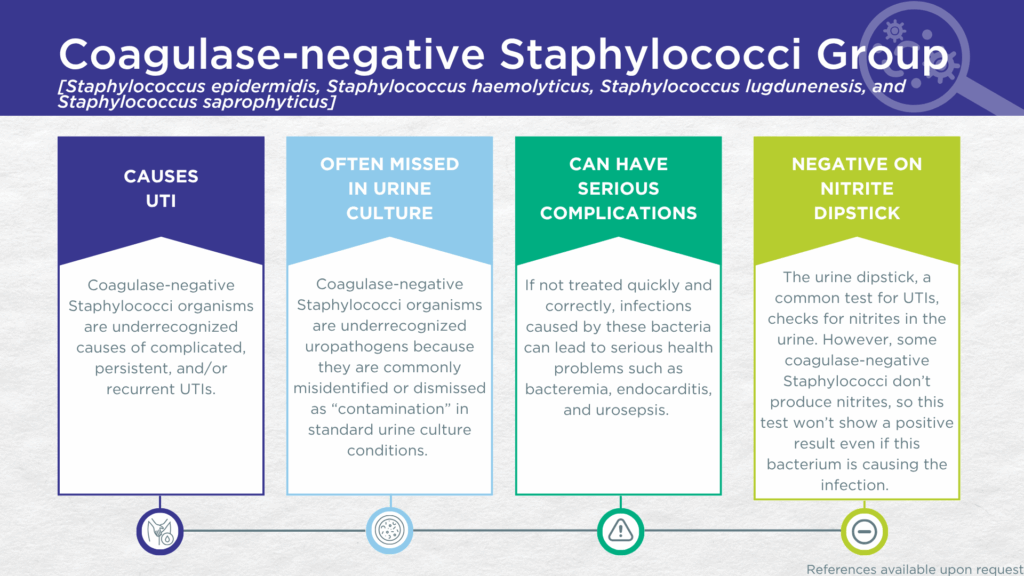
- CoNS are biofilm-forming, gram-positive microorganisms that may be urease-positive.
- CoNS are occasionally nitrite-negative on urinalysis dipsticks.
- CoNS are commonly dismissed as contaminants in standard urine culture conditions.
- CoNS are associated with recurrent UTIs in post-pubertal women and with complicated and persistent UTIs in men and children.
- In symptomatic UTI patients, CoNS:
- Are not a contaminant (is found in catheter-collected urine specimens).
- Are viable (can grow out on culture).
- Are pathogenic (associated with elevated urine biomarkers of infection).
- Reported severe complications of CoNS UTI include bacteremia endocarditis, and urosepsis.
Bacterial Characteristics
Gram-stain
Gram-positive (all)
Morphology
Coccus (all)
Growth Requirements
Non-fastidious (all grow well in standard urine culture conditions)
Facultative anaerobe
Nitrate Reduction
Yes (except S. saprophyticus is variable for this phenotype)
Urease
Positive (S. epidermidis and S. saprophyticus)
Negative (S. haemolyticus and S. lugdunenesis)
Biofilm Formation
Yes (all)
Pathogenicity
Colonizer or Pathobiont
Clinical Relevance in UTI
Coagulase-negative Staphylococci (CoNS) is a group of Staphylococcus species that are grouped according to the shared characteristic they are named for: lack of the virulence factor coagulase.[1] They are traditionally described as gram-positive commensals of the human skin microbiome.[2] In the Guidance® UTI assay, this group term specifically encompasses four species, S. epidermidis, S. haemolyticus, S. lugdunenesis, and S. saprophyticus.
S. epidermidis
S. epidermidis is a urease-positive microorganism [3] associated with biofilm formation in catheter-associated UTI [4] and with calcifications in chronic bacterial prostatitis [5]. S. epidermidis is also associated with UTI and pyelonephritis in young children, adolescent males, and children with urinary tract abnormalities [6–8]. S. epidermidis was also reported in an adult female with recurrent UTI [9] and in two adult males with nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis, and bacteremia secondary to UTI.[10] Additionally, in a sequencing-based study, S. epidermidis was detected only in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) patient urine specimens but not in asymptomatic controls, suggesting that these patients’ lower urinary tract symptoms were due to unrecognized/untreated S. epidermidis UTIs.[11] S. epidermidis UTI isolates are frequently multi-drug resistant.[12]
S. haemolyticus
S. haemolyticus is associated with UTI in pregnant women [13] and with UTI and pyelonephritis in young children, adolescent males, and children with urinary tract abnormalities [6] S. haemolyticus was also reported in an adult female with recurrent UTI, [14] in an adult male with persistent UTI,[15] and in an adult male with urosepsis, urinary blockage, and prostatic abscess secondary to UTI.[16] S. haemolyticus UTI isolates are frequently multi-drug resistant.[12,17,18]
S. lugdunenesis
S. lugdunenesis is associated with UTI, and specifically with pyelonephritis, in adult and adolescent males, as well as children of any sex with underlying urinary tract abnormalities.[6,19] S. lugdunenesis was also reported in an immune-compromised adult female [20] and in five adult females with lower urinary tract symptoms.[14] Furthermore, S. lugdunenesis was identified by expanded quantitative urine culture (EQUC) in catheter-obtained urine samples from UTI patients but not asymptomatic controls.[21,22] S. lugdunenesis UTI, especially pyelonephritis, can lead to bacteremia [23] and S. lugdunenesis bacteremia is associated with severe complications, including aggressive endocarditis [24,25] and pericarditis [26].
S. saprophyticus
S. saprophyticus is a urease-positive,[3] biofilm-forming [27,28] microorganism. S. saprophyticus is considered a common cause of acute uncomplicated cystitis [6] and recurrent UTI [29] in post-pubertal adolescent and young-adult females. S. saprophyticus was also reported to cause pyelonephritis, bacteremia, and urosepsis in a pregnant 17-year-old female [30] and an immune-compromised 64-year-old female [31]. S. saprophyticus UTI isolates are frequently multi-drug resistant.[27,28]
The Coagulase-negative Staphylococci Group
CoNS UTIs are likely significantly underdiagnosed for a couple of reasons. Firstly, some strains of the S. saprophyticus species lack nitrate reductase activity, so screening strategies involving urinalysis for nitrite positivity may be false-negative.[3,32] Secondly, although these organisms grow readily in standard urine culture conditions, they are commonly dismissed as irrelevant gram-positive commensal organisms of the urogenital microbiome and labeled as a “contaminant”.[33]
However, in a study of older adult males and females with clinically suspected complicated UTI, CoNS was detected in both midstream voided and in-and-out-catheter collected specimens indicating that it was truly present in the bladder, not simply a contaminant picked up during voiding.[34] Furthermore, elevated markers of immune system activation in the urinary tract have been measured from the same clinical urine specimens in which CoNS was detected, indicating that the presence of CoNS was associated with an immune response to urinary tract infection.[35–37]
Despite their reputation as contaminants, CoNS (S. epidermidis, S. haemolyticus, S. lugdunenesis, and S. saprophyticus) are all associated with complicated, persistent, and/or recurrent UTIs, as well as with severe complications such as bacteremia and endocarditis. Together, these findings indicate that CoNS should be seriously considered as a uropathogen and demonstrate the value of detecting these organisms, particularly in individuals with immune compromise or other risk factors for complicated, persistent, or recurrent UTI.
Treatment
Evidence of Efficacy (Checkmarks): Doxycycline, Linezolid, Nitrofurantoin, Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim, Trimethoprim, and Vancomycin.
1. Michels, R.; Last, K.; Becker, S.L.; Papan, C. Update on Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—What the Clinician Should Know. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 830, doi:10.3390/microorganisms9040830.
2. Chowdhury, S.; Fong, S.S. Computational Modeling of the Human Microbiome. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 197, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8020197.
3. BacDive | The Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Available online: https://bacdive.dsmz.de/ (accessed on 11 February 2025).
4. Curtin, J.J.; Donlan, R.M. Using Bacteriophages To Reduce Formation of Catheter-Associated Biofilms by Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1268–1275, doi:10.1128/aac.50.4.1268-1275.2006.
5. Mazzoli, S. Biofilms in Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis (NIH‐II) and in Prostatic Calcifications. FEMS Immunol. Méd. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 337–344, doi:10.1111/j.1574-695x.2010.00659.x.
6. Megged, O. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci: A Rare Cause of Urinary Tract Infections in Children with Consequences on Clinical Practice. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 1099–1104, doi:10.1007/s00431-021-04308-4.
7. Steele, G.; Tan, W.; Saleeby, C.E.; Zanger, K. Staphylococcus Epidermidis as a Uropathogen in Children. Urology 2023, 176, 183–186, doi:10.1016/j.urology.2023.02.021.
8. Parsons, E.; Albert, C.; Forouhar, M.; Kunz, A.; Sainato, R. Recurrent Severe Staphylococcus Epidermidis Urinary Tract Infections in a 7-Year-Old Boy. Clin. Pediatr. 2021, 60, 346–349, doi:10.1177/00099228211021277.
9. Jablonska, S.; Wolfe, A.J.; Putonti, C. Draft Genome Sequence of Staphylococcus Epidermidis UMB7543, Isolated from a Female Patient with Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 11, e00962-22, doi:10.1128/mra.00962-22.
10. Yogo, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Sumiyoshi, S.; Iwamoto, N.; Aoki, K.; Motobayashi, H.; Tochitani, K.; Shimizu, T.; Murashima, T.; Nishikawa, N.; et al. Two Cases of Pyelonephritis with Bacteremia by Staphylococcus Epidermidis in Male Patients with Nephrolithiasis: Case Reports and a Literature Review. J. Infect. Chemother. 2022, 28, 1189–1192, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2022.04.030.
11. Jacobs, K.M.; Price, T.K.; Thomas-White, K.; Halverson, T.; Davies, A.; Myers, D.L.; Wolfe, A.J. Cultivable Bacteria in Urine of Women With Interstitial Cystitis: (Not) What We Expected. Female Pelvic Med. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 27, 322–327, doi:10.1097/spv.0000000000000854.
12. Phillip, S.; Mushi, M.F.; Decano, A.G.; Seni, J.; Mmbaga, B.T.; Kumburu, H.; Konje, E.T.; Mwanga, J.R.; Kidenya, B.R.; Msemwa, B.; et al. Molecular Characterizations of the Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Species Causing Urinary Tract Infection in Tanzania: A Laboratory-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Pathogens 2023, 12, 180, doi:10.3390/pathogens12020180.
13. Aziz, L.M.; Iraq, D. of B., College of Applied Sciences, University of Fallujah,; Alhachami, F.R.; Iraq, D. of B., College of Education for Pure Science, Wasit University, Wasit,; Abdullah, M.A.; Iraq, D. of M., Ninevah College of Medicine, Ninevah University, Mosul,; Abed, A.S.; Iraq, J.I.H.U. of M. and P.S., Najaf,; Ali, M.H.; Iraq, D.-Q.H.D., Iraqi Ministry of Health, Nasiriya,; et al. Molecular Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Staphylococcus Haemolyticus in Pregnant Women with Urinary Tract Infections. Iran. J. Méd. Microbiol. 2023, 17, 354–360, doi:10.30699/ijmm.17.3.354.
14. Appleberry, H.; Anjum, H.; Cage, T.; Jarm, K.; Khan, H.; Proctor, L.; Saroca, J.; Wolfe, A.J.; Putonti, C.; Kula, A. Draft Genomes of One Staphylococcus Haemolyticus and Five Staphylococcus Lugdunensis Strains Isolated from Catheterized Urine Samples of Females. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2024, 13, e00497-24, doi:10.1128/mra.00497-24.
15. Gunn, B.A.; Davis, C.E. Staphylococcus Haemolyticus Urinary Tract Infection in a Male Patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 1055–1057, doi:10.1128/jcm.26.5.1055-1057.1988.
16. Bermudez, M.; Epstein, S.B.; Guevara, N.; Pedraza, L.; Dahdouh, M.; Awad, I. Prostatic Abscess Secondary to Staphylococcus Haemolyticus and Escherichia Coli: A Case Report. Cureus 2023, 15, e40406, doi:10.7759/cureus.40406.
17. Aniba, R.; Dihmane, A.; Raqraq, H.; Ressmi, A.; Nayme, K.; Timinouni, M.; Barguigua, A. Molecular and Phenotypic Characterization of Biofilm Formation and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Uropathogenic Staphylococcus Haemolyticus Isolates in Casablanca, Morocco. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 110, 116483, doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2024.116483.
18. Bangladesh, D. of V. and A.S., Faculty of Agriculture, Rajshahi University, Rajshahi-6205,; MH, H.; ML, M.; S, S.; Australia, D. of P., Anatomy and Microbiology, School of Life Sciences, La Trobe University, Melbourne VIC 3086,; M, S.; Kingdom, S. doctor in A.M., Leighton Hospital, Middlewich Rd, United; MJA, S.; Australia, S. of E. and S. (ESC), and Queensland Micro-and Nanotechnology Centre (QMNC) Griffith University, Nathan Campus, 170 Kessels Road, QLD 4111, Molecular Characterization and Antibiogram Profiling of Multidrug Resistant Staphylococcus Haemolyticus Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infection in Bangladesh. J. Bacteriol. Mycol. 2021, 8, doi:10.26420/jbacteriolmycol.2021.1166.
19. Chiu, K.H.Y.; Lam, R.P.K.; Chan, E.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Emergence of Staphylococcus Lugdunensis as a Cause of Urinary Tract Infection: Results of the Routine Use of MALDI-TOF MS. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 381, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8030381.
20. Bobde, R.; Berger, J.I.; Jalil, U.; Kalaydjian, G. Staphylococcus Lugdunensis Urinary Tract Infection With Associated Neutropenic Fever. Cureus 2022, 14, e21432, doi:10.7759/cureus.21432.
21. Price, T.K.; Hilt, E.E.; Dune, T.J.; Mueller, E.R.; Wolfe, A.J.; Brubaker, L. Urine Trouble: Should We Think Differently about UTI? Int Urogynecol J 2018, 29, 205–210, doi:10.1007/s00192-017-3528-8.
22. Price, T.K.; Dune, T.; Hilt, E.E.; Thomas-White, K.J.; Kliethermes, S.; Brincat, C.; Brubaker, L.; Wolfe, A.J.; Mueller, E.R.; Schreckenberger, P.C. The Clinical Urine Culture: Enhanced Techniques Improve Detection of Clinically Relevant Microorganisms. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2016, 54, 1216–1222, doi:10.1128/jcm.00044-16.
23. Hunter, N.; Kusnik, A.; Proia, L. A Frequently Overlooked Contaminant: A Case of Staphylococcus Lugdunensis Bacteremia. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2023, 13, 107–108, doi:10.55729/2000-9666.1201.
24. Aldman, M.H.; Rasmussen, M.; Olaison, L.; Påhlman, L.I. Endocarditis Due to Staphylococcus Lugdunensis—a Retrospective National Registry–Based Study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 1103–1106, doi:10.1007/s10096-020-04134-w.
25. Non, L.R.; Santos, C.A.Q. The Occurrence of Infective Endocarditis with Staphylococcus Lugdunensis Bacteremia: A Retrospective Cohort Study and Systematic Review. J. Infect. 2017, 74, 179–186, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2016.10.003.
26. Khalaf, S.A.; Mansour, A.; Perveze, I.; Fender, B.; Walker, D.R.; Dandachi, D. Staphylococcus Lugdunensis as Cause of Septic Pericarditis. Mo. Med. 2021, 118, 552–555.
27. Rafiee, M.; Ghaemi, E.A. Detection of Virulence Genes among Staphylococcus Saprophyticus Isolated from Women with Urinary Tract Infections: First Report from Iran. BMC Res. Notes 2023, 16, 206, doi:10.1186/s13104-023-06481-1.
28. Hashemzadeh, M.; Dezfuli, A.A.Z.; Nashibi, R.; Jahangirimehr, F.; Akbarian, Z.A. Study of Biofilm Formation, Structure and Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus Saprophyticus Strains Causing Urinary Tract Infection in Women in Ahvaz, Iran. N. Microbes N. Infect. 2021, 39, 100831, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2020.100831.
29. Latham, R.H.; Running, K.; Stamm, W.E. Urinary Tract Infections in Young Adult Women Caused by Staphylococcus Saprophyticus. JAMA 1983, 250, 3063–3066, doi:10.1001/jama.1983.03340220031028.
30. Olsen, R.C.; Abbott, B. Staphylococcus Saprophyticus , an Unusual Cause of Pyelonephritis and Sepsis in Pregnancy. Ann. Intern. Med.: Clin. Cases 2024, 3, doi:10.7326/aimcc.2023.0613.
31. Yoshida, K.; Okawa, N.; Nobuaki, T.; Otsuka, Y.; Hosokawa, N. A Case of Staphylococcus Saprophyticus Bacteremia Caused by Obstructive Pyelonephritis. J. Infect. Chemother. 2025, 31, 102629, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2025.102629.
32. BioCyc Pathway/Genome Database Collection Available online: https://biocyc.org/ (accessed on 11 February 2025).
33. Maskell, R. IMPORTANCE OF COAGULASE-NEGATIVE STAPHYLOCOCCI AS PATHOGENS IN THE URINARY TRACT. Lancet 1974, 303, 1155–1158, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90634-5.
34. Wang, D.; Haley, E.; Luke, N.; Mathur, M.; Festa, R.; Zhao, X.; Anderson, L.A.; Allison, J.L.; Stebbins, K.L.; Diaz, M.J.; et al. Emerging and Fastidious Uropathogens Were Detected by M-PCR with Similar Prevalence and Cell Density in Catheter and Midstream Voided Urine Indicating the Importance of These Microbes in Causing UTIs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, Volume 16, 7775–7795, doi:10.2147/idr.s429990.
35. Haley, E.; Luke, N.; Mathur, M.; Festa, R.A.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Anderson, L.A.; Baunoch, D. The Prevalence and Association of Different Uropathogens Detected by M-PCR with Infection-Associated Urine Biomarkers in Urinary Tract Infections. Res. Rep. Urol. 2024, 16, 19–29, doi:10.2147/rru.s443361.
36. Akhlaghpour, M.; Haley, E.; Parnell, L.; Luke, N.; Mathur, M.; Festa, R.A.; Percaccio, M.; Magallon, J.; Remedios-Chan, M.; Rosas, A.; et al. Urine Biomarkers Individually and as a Consensus Model Show High Sensitivity and Specificity for Detecting UTIs. BMC Infect Dis 2024, 24, 153, doi:10.1186/s12879-024-09044-2.
37. Parnell, L.K.D.; Luke, N.; Mathur, M.; Festa, R.A.; Haley, E.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Anderson, L.; Baunoch, D. Elevated UTI Biomarkers in Symptomatic Patients with Urine Microbial Densities of 10,000 CFU/ML Indicate a Lower Threshold for Diagnosing UTIs. MDPI 2023, 13, 1–15, doi:10.3390/diagnostics13162688.
Dr. Emery Haley is a scientific writing specialist with over ten years of experience in translational cell and molecular biology. As both a former laboratory scientist and an experienced science communicator, Dr. Haley is passionate about making complex research clear, approachable, and relevant. Their work has been published in over 10 papers and focuses on bridging the gap between the lab and real-world patient care to help drive better health outcomes.