K. pneumoniae
Emery Haley, PhD, Scientific Writing Specialist
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Clinical Summary
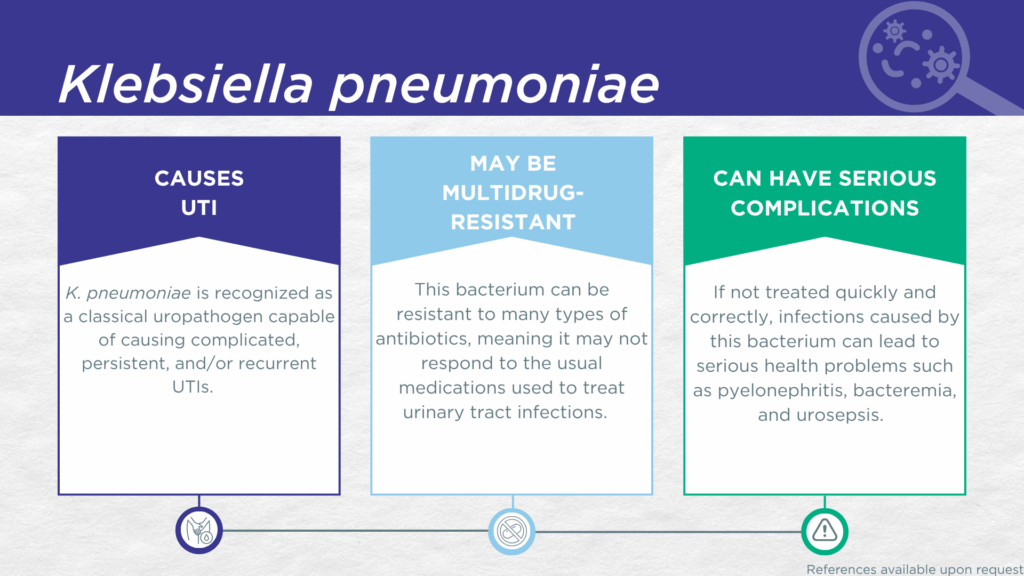
- K. pneumoniae is recognized as a classical, urease-positive, gram-negative, biofilm-forming, uropathogen.
- K. pneumoniae is primarily associated with recurrent UTIs and complicated UTIs in individuals with risk-factors such as indwelling catheters, immunocompromising comorbidities, or urinary tract abnormalities.
- In symptomatic UTI patients, K. pneumoniae:
- Is not a contaminant (is found in catheter-collected urine specimens).
- Is viable (can grow out on culture).
- Is pathogenic (associated with elevated urine biomarkers of infection).
- Reported severe complications of K. pneumoniae UTI include pyelonephritis, bacteremia, urosepsis, and death.
- Multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae is a significant and well-studied global health threat.
Bacterial Characteristics
Gram-stain
Gram-negative
Morphology
Bacillus
Growth Requirements
Non-fastidious (grows well in standard urine culture conditions)
Facultative anaerobe
Nitrate Reduction
Yes
Urease
Positive
Biofilm Formation
Yes
Pathogenicity
Colonizer or Pathobiont
Clinical Relevance in UTI
K. pneumoniae is a urease-positive,[1]gram-negative, biofilm-forming, microorganism classically recognized as a common uropathogen. K. pneumoniae is capable of invading epithelial cells of the urinary tract, forming intracellular reservoirs presumed responsible for persistent and recurrent K. pneumoniae UTIs.[2–4] K. pneumoniae is also a common cause of complicated UTIs among individuals who are immunocompromised or who have risk factors such as urinary tract abnormalities. [4–7] Lastly, K. pneumoniae is associated with hard-to-treat multidrug-resistant catheter-associated UTIs (CAUTIs) and hospital-acquired UTIs (HAUTIs).[8–10] Indeed, K. pneumoniae is one of the six so-called “ESKAPE pathogens” identified as critical multi-drug resistant bacteria requiring urgent development of effective therapeutics.[11]
In preclinical studies of UTI, uropathogenic K. pneumoniae exhibits virulence factors including type 1 pili and adhesins promoting adherence to bladder epithelial cells and a capsule that promotes immune evasion.[12] In preclinical models, K. pneumoniae invaded bladder epithelial cells[13] and also exhibited antagonism with Enterococcus species, E. coli, and P. mirabilis.[14]
In a study of older adult males and females with clinically suspected complicated UTI, K. pneumoniae was detected in both midstream voided and in-and-out-catheter collected specimens indicating that it was truly present in the bladder, not simply a contaminant picked up during voiding.[15] Furthermore, elevated markers of immune system activation in the urinary tract have been measured from the same clinical urine specimens in which K. pneumoniae was detected, indicating that the presence of K. pneumoniae was associated with an immune response to urinary tract infection.[16–18]
Severe reported complications of K. pneumoniae UTI include pyelonephritis, bacteremia, urosepsis, and death.[7,9,19,20] Together, these findings indicate that K. pneumoniae should be seriously considered as a uropathogen and demonstrate the value of detecting this organism, particularly in individuals with indwelling catheters, urinary tract abnormalities, immunocompromise, or other risk factors for complicated or experiencing recurrent UTI.
Treatment
Evidence of Efficacy (Checkmarks): Amoxicillin/Clavulanate, Ampicillin/Sulbactam, Cefaclor, Cefazolin, Cefepime, Ceftazidime, Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline, Gentamicin, Levofloxacin, Meropenem, Nitrofurantoin, Piperacillin/Tazobactam, Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim, and Trimethoprim.
1. BacDive | The Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Available online: https://bacdive.dsmz.de/ (accessed on 11 February 2025).
2. Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Tall, B.D. Invasion of Cultured Human Epithelial Cells by Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolated from the Urinary Tract. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 2950–2958, doi:10.1128/iai.65.7.2950-2958.1997.
3. Le, T.; Nang, S.C.; Zhao, J.; Yu, H.H.; Li, J.; Gill, J.J.; Liu, M.; Aslam, S. Therapeutic Potential of Intravenous Phage as Standalone Therapy for Recurrent Drug-Resistant Urinary Tract Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e00037-23, doi:10.1128/aac.00037-23.
4. Lin, W.H.; Kao, C.Y.; Yang, D.C.; Tseng, C.C.; Wu, A.B.; Teng, C.H.; Wang, M.C.; Wu, J.J. Clinical and Microbiological Characteristics of Klebsiella Pneumoniae from Community-Acquired Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1533–1539, doi:10.1007/s10096-014-2100-4.
5. CRISTEA, O.M.; AVRĂMESCU, C.S.; BĂLĂȘOIU, M.; POPESCU, F.D.; POPESCU, F.; AMZOIU, M.O. Urinary Tract Infection with Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Heal. Sci. J. 2017, 43, 137–148, doi:10.12865/chsj.43.02.06.
6. Zafar, S.; Hanif, S.; Akhtar, H.; Faryal, R. Emergence of Hypervirulent K. Pneumoniae Causing Complicated UTI in Kidney Stone Patients. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103647, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103647.
7. Parente, G.; Gargano, T.; Pavia, S.; Cordola, C.; Vastano, M.; Baccelli, F.; Gallotta, G.; Bruni, L.; Corvaglia, A.; Lima, M. Pyelonephritis in Pediatric Uropathic Patients: Differences from Community-Acquired Ones and Therapeutic Protocol Considerations. A 10-Year Single-Center Retrospective Study. Children 2021, 8, 436, doi:10.3390/children8060436.
8. Obaid, N.A.; Abuhussain, S.A.; Mulibari, K.K.; Alshanqiti, F.; Malibari, S.A.; Althobaiti, S.S.; Alansari, M.; Muneef, E.; Almatrafi, L.; Alqarzi, A.; et al. Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens Related to Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections in Intensive Care Units: A Multi-Center Retrospective Study in the Western Region of Saudi Arabia. Clin. Epidemiology Glob. Heal. 2023, 21, 101291, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2023.101291.
9. Kayaaslan, B.; Oktay, Z.; Hasanoglu, I.; Kalem, A.K.; Eser, F.; Ayhan, M.; Guner, R. Increasing Rates of Extended-Spectrum B-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia Coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Uncomplicated and Complicated Acute Pyelonephritis and Evaluation of Empirical Treatments Based on Culture Results. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 41, 421–430, doi:10.1007/s10096-021-04392-2.
10. D’Incau, S.; Atkinson, A.; Leitner, L.; Kronenberg, A.; Kessler, T.M.; Marschall, J. Bacterial Species and Antimicrobial Resistance Differ between Catheter and Non–Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections: Data from a National Surveillance Network. Antimicrob. Steward. Healthc. Epidemiology : ASHE 2023, 3, e55, doi:10.1017/ash.2022.340.
11. Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE Pathogens: Antimicrobial Resistance, Epidemiology, Clinical Impact and Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616, doi:10.1038/s41579-024-01054-w.
12. Joseph, L.; Merciecca, T.; Forestier, C.; Balestrino, D.; Miquel, S. From Klebsiella Pneumoniae Colonization to Dissemination: An Overview of Studies Implementing Murine Models. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1282, doi:10.3390/microorganisms9061282.
13. Abell-King, C.; Pokhrel, A.; Rice, S.A.; Duggin, I.G.; Söderström, B. Multispecies Bacterial Invasion of Human Host Cells. Pathog. Dis. 2024, 82, ftae012, doi:10.1093/femspd/ftae012.
14. Gaston, J.R.; Johnson, A.O.; Bair, K.L.; White, A.N.; Armbruster, C.E. Polymicrobial Interactions in the Urinary Tract: Is the Enemy of My Enemy My Friend? Infect Immun 2021, 89, doi:10.1128/iai.00652-20.
15. Wang, D.; Haley, E.; Luke, N.; Mathur, M.; Festa, R.; Zhao, X.; Anderson, L.A.; Allison, J.L.; Stebbins, K.L.; Diaz, M.J.; et al. Emerging and Fastidious Uropathogens Were Detected by M-PCR with Similar Prevalence and Cell Density in Catheter and Midstream Voided Urine Indicating the Importance of These Microbes in Causing UTIs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, Volume 16, 7775–7795, doi:10.2147/idr.s429990.
16. Haley, E.; Luke, N.; Mathur, M.; Festa, R.A.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Anderson, L.A.; Baunoch, D. The Prevalence and Association of Different Uropathogens Detected by M-PCR with Infection-Associated Urine Biomarkers in Urinary Tract Infections. Res. Rep. Urol. 2024, 16, 19–29, doi:10.2147/rru.s443361.
17. Akhlaghpour, M.; Haley, E.; Parnell, L.; Luke, N.; Mathur, M.; Festa, R.A.; Percaccio, M.; Magallon, J.; Remedios-Chan, M.; Rosas, A.; et al. Urine Biomarkers Individually and as a Consensus Model Show High Sensitivity and Specificity for Detecting UTIs. BMC Infect Dis 2024, 24, 153, doi:10.1186/s12879-024-09044-2.
18. Parnell, L.K.D.; Luke, N.; Mathur, M.; Festa, R.A.; Haley, E.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Anderson, L.; Baunoch, D. Elevated UTI Biomarkers in Symptomatic Patients with Urine Microbial Densities of 10,000 CFU/ML Indicate a Lower Threshold for Diagnosing UTIs. MDPI 2023, 13, 1–15, doi:10.3390/diagnostics13162688.
19. Wu, Y.; Li, P.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, B.; Zhou, W.; Duan, F.; Wang, G.; Li, J. Four-Year Variation in Pathogen Distribution and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Urosepsis: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, 20499361241248056, doi:10.1177/20499361241248058.
20. Shahab, K.; Mufti, A.Z.; Iqbal, M.A.; Roghani, M.; Zeb, F.; Amin, U. Assessment of Microbial Diversity Pattern of Sensitivity and Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Patients Admitted with Urosepsis. Ann. PIMS-Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Méd. Univ. 2023, 19, 339–345, doi:10.48036/apims.v19i3.924.
Dr. Emery Haley is a scientific writing specialist with over ten years of experience in translational cell and molecular biology. As both a former laboratory scientist and an experienced science communicator, Dr. Haley is passionate about making complex research clear, approachable, and relevant. Their work has been published in over 10 papers and focuses on bridging the gap between the lab and real-world patient care to help drive better health outcomes.