
More informed treatment decisions
with P-AST™
Precision diagnostic testing with rapid results for the management of complicated, recurrent or persistent UTIs and elevated risk patients
Organism identification (PCR)
26 individual organisms and 3 bacterial groups, developed using an evidence based analysis of uropathogens
Resistance gene detection (PCR)
32 resistance genes and 6 different classes of antibiotics
Pooled antibiotic susceptibility testing (P-AST™)
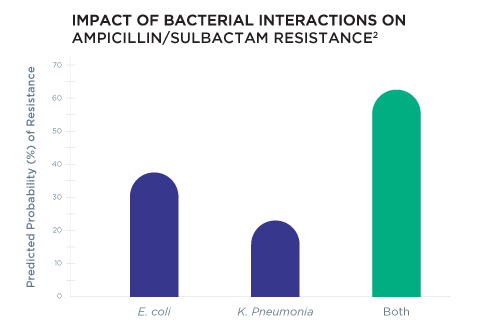
Pooled Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (P-AST™) accounts for bacterial interactions that occur in polymicrobial infections that may alter antibiotic resistance
Delivers results in an easy to read report in less than one day from receipt at lab†
Organism
identification
(PCR)
27 individual organisms and 3 bacterial groups, developed using an evidence based analysis of uropathogens
Resistance
gene
detection
(PCR)
32 resistance genes and 6 different classes of antibiotics
Pooled
antibiotic
susceptibility
testing
(P-AST™)
Pooled Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (P-AST™) accounts for bacterial interactions that occur in polymicrobial infections that may alter antibiotic resistance
Delivers results in an easy to read report in less than one day from receipt at lab†
Guidance® UTI is an advanced test that better addresses polymicrobial infections in difficult cases, where bacterial interactions can impact antibiotic resistance.
Guidance® UTI provides personalized results in less than one day from receipt at lab, while culture can take 3-5 days, reducing the need for empiric therapy and supporting antibiotic stewardship initiatives.
Results are summarized in an easy- to-read report showing therapy options based on the patient’s individual infection.
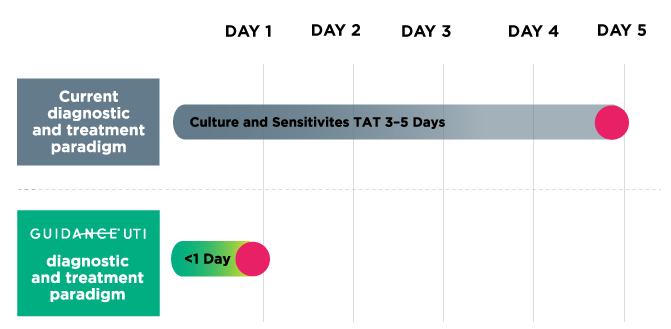
Guidance® UTI uses PCR technology to identify commonly tested uropathogens, including fastidious bacteria and yeasts, that are difficult to detect by culture. Guidance UTI has demonstrated 95% sensitivity when identifying organisms, which is 43% more sensitive than culture.1 High sensitivity helps ensure accurate pathogen identification and UTI diagnosis.
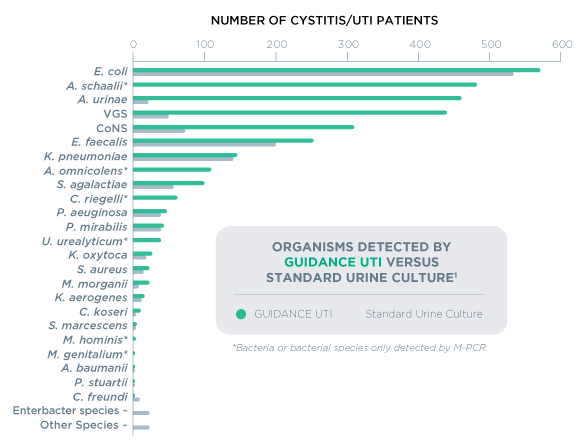
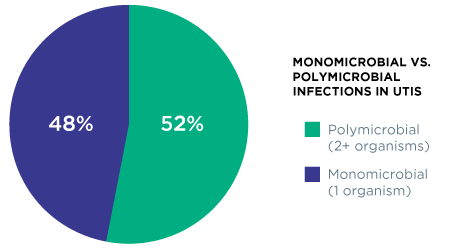
Guidance® UTI identifies specific pathogenic organisms and effective treatments for polymicrobial infections, which have been shown to occur in up to 52% of positive cases.1 While culture may return these results as “contaminated” or “mixed flora”, Guidance UTI identifies the specific uropathogens in the specimen – even when multiple organisms are present.
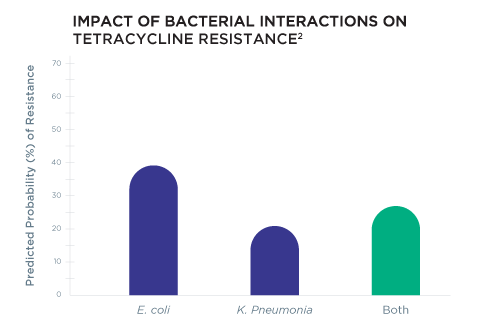
Rather than relying on resistance gene information alone, Guidance® UTI provides personalized therapy options by using Pooled Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (P-AST™), a unique technology that accounts for bacterial interactions that occur in polymicrobial infections that may alter antibiotic resistance.2
Real World Evidence
Guidance® UTI testing is associated with reductions in critical adverse outcomes, healthcare resource utilization and cost for complicated (cUTI).
Study size: for standard urine culture (N=678) or Guidance UTI® (N=69)

13%
lower rate of outpatient emergency visits

67%
lower inpatient admissions rate

NO
urosepsis, urgent care and skilled nursing facility admissions for every 1,000 patients in this study

$463.46
savings per cUTI patient tested with Guidance UTI (p=0.043)

42%
reduction in visits to emergency department, inpatient hospital, urgent care and SNF

$11.6 MIL
SAVINGS
for 25,000 cUTI cases
Reference: Aparna Ashok, Dicken Ko, Providence RI, Emily Lukacz, La Jolla, CA, Annah Vollstedt, Iowa City, IA, Iver Juster, San Rafael, CA, Timothy Niecko, Tierra Verde, FL, David Baunoch, Trabuco Canyon, CA, Mohit Mathur, Irvine, CA. Comparison of Guidance® UTI and standard urine culture for rates of sepsis, hospitalization and other adverse outcomes in complicated urinary tract infections [abstract]. Journal of Urology. AUA Annual Meeting Program Abstracts 2022. 1 May 2022. Volume 207 Issue Supplement 5 May 2022.
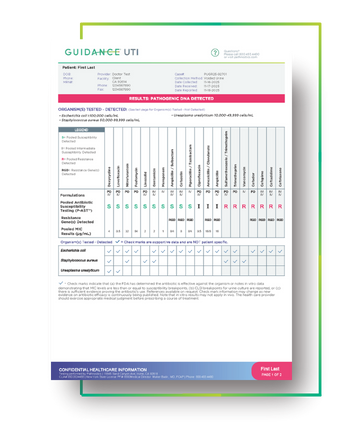
View a sample report
The Guidance® UTI report displays personalized therapy options.
The same Guidance® UTI results you trust, from the comfort of home
Whether it’s busy schedules, limited mobility, or the patient was simply unable to leave a sample at the time of the office visit, incorporating Guidance® UTI testing from the comfort of home can facilitate access to care as well as reduce the risk of exposure for both patients and providers. After a provider places an order for a home kit, the Pathnostics team will take it from there!

Patient Assessment
The provider determines if Guidance® UTI testing is appropriate for the patient.

One step ordering
The provider completes a Guidance® UTI test requisition and faxes it to Pathnostics.

Signature service
Pathnostics will call each patient to review specimen collection instructions, coordinate same-day pickup for overnight shipping, and answer questions about the process.

Fast turnaround time
Once received at the lab, Guidance® UTI home kits have the same less than one day† turnaround you’ve come to depend on with our in-office results.
Frequently Asked Questions
Pathnostics’ GUIDANCE® UTI Test utilizes PCR amplification for the targeted detection of agents. Pathogens are reported in ranges of organism(s) per milliliter of urine.
In addition to the often-tested organisms Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus, we also test for an extremely comprehensive list of pathogens.
BACTERIAL/YEAST ORGANISMS:
- Acinetobacter baumannii
- Actinotignum schaalii
- Aerococcus urinae
- Alloscardovia omnicolens
- Candida albicans
- Candida auris
- Candida glabrata
- Candida parapsilosis
- Citrobacter freundii
- Citrobacter koseri
- Corynebacterium riegelii
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Enterococcus faecium
- Escherichia coli
- Gardnerella vaginalis
- Klebsiella oxytoca
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Morganella morganii
- Mycoplasma hominis
- Proteus mirabilis
- Providencia stuartii
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Serratia marcescens
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus agalactiae
- Ureaplasma urealyticum
BACTERIAL GROUPS:
- Coagulase-negative staphylococci*
- Viridans group streptococci†
- Enterobacter group‡
- ESBL PHENOTYPE
ESBL phenotypic assay will be performed when E. coli, Klebsiella, Enterocobacter, Citrobacter, Proteus, Acinetobacter, or Pseudomonas are detected - MRSA PHENOTYPE
MRSA phenotypic assay will be performed when Staphylococcus aureus and the mecA gene are detected.
*Coagulase-negative staphylococci: Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus lugdunenesis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus
†Viridans group streptococci: Streptococcus anginosus,
Streptococcus oralis, Streptococcus pasteuranus
‡Enterobacter group: Klebsiella aerogenes (formally known as Enterobacter aerogenes), Enterobacter cloacae
We leverage a dual assessment—genotype resistance and Pooled Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (P-AST™)—to uncover more effective, personalized therapy options.
Pooled Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (P-AST™) includes:
- Ampicillin (PO/IV)
- Ampicillin/Sulbactam (IV)
- Amoxicillin/Clavulanate (PO)
- Cefaclor (PO)
- Cefazolin (IM/IV)
- Cefepime (IM/IV)
- Ceftazidime (IV)
- Ceftriaxone (IM/IV)
- Ciprofloxacin (PO/IV)
- Doxycycline (PO/IV)
- Fosfomycin (PO)
- Gentamicin (IM/IV)
- Levofloxacin (PO/IV)
- Linezolid (PO/IV)
- Meropenem (IV)
- Nitrofurantoin (PO)
- Piperacillin/Tazobactam (IV)
- Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim (PO/IV)
- Trimethoprim (PO)
- Vancomycin (IV)
Genotype antibiotic resistance genes include:
- Ampicillin
- Carbapenem
- Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase
- Methicillin
- Quinolinone/Fluoroquinolone
- Vancomycin
Pathnostics’ GUIDANCE® UTI Test utilizes PCR amplification for the targeted detection of 32 antibiotic resistance genes. across 6 antibiotic classes. Results are reported as “detected” or “not detected”.
- Ampicillin
- Carbapenem
- Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase
- Methicillin
- Quinolinone/Fluoroquinolone
- Vancomycin
Please watch our instruction video on how to collect a urine sample at the provider office.
contact sales
Ready to provide your patients with personalized therapy right from the start?
References:
1. Vollstedt A, Baunoch D, Wojno KJ, Luke N, Cline K, et al. (2020). Multisite Prospective Comparison of Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing with Urine Culture for Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections in Symptomatic Patients. J Sur urology, JSU-102. DOI: 10.29011/ JSU-102.100002
2. Vollstedt A, Baunoch D, Wolfe A, Luke N, Wojno KJ, et al. (2020). Bacterial Interactions as Detected by Pooled Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (P-AST) in Polymicrobial Urine Specimens. J Sur urology, JSU-101. DOI: 10.29011/JSU-101.100001
3. Vos MG de, Zagorski M, McNally A, Bollenbach T (2017) Interaction networks, ecological stability, and collective antibiotic tolerance in polymicrobial infections. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 114:10666–10671. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1713372114
† When specimen collected as instructed

